Workshop summary
2.6.1 Day 1: Raw sequence to gene counts
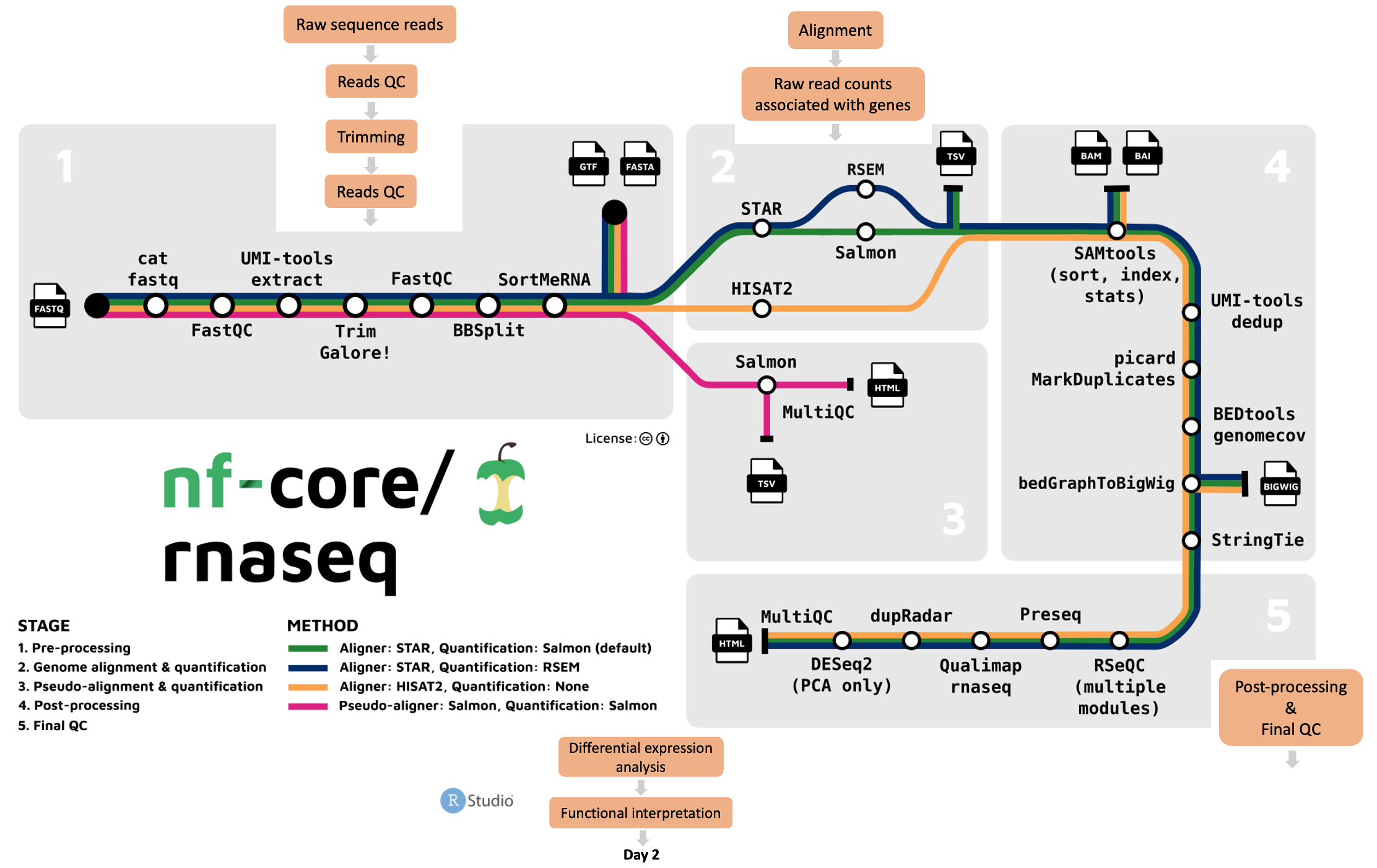
On Day 1 we used the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline to convert raw RNAseq data into raw counts.
We discussed the following essential steps in a RNAseq analysis workflow:
- Check the quality of raw-reads.
- Trim the raw-reads to get rid of bad-quality read-regions and/or bad-quality reads.
- Align the trimmed-reads to reference sequence to identify where they belong
- Quantify the aligned reads to get gene-level read-counts.
Next:
- We discussed the workflow management tool nextflow which is used for automated, reproducible, flexible and portable analysis.
- We excecuted the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline and interpreted its outputs.
2.6.2 Day 2: Counts to genes and functional enrichments
On Day 2 we used the raw counts to identify the differentially expressed genes and highlighted the relevant functions.
The following steps were identified to be essential:
- Perform an exploratory analysis of the count data for quality control.
- Analyse the count data to identify differentially expressed genes.
- Identify functional enrichments from differentially expressed genes.
- We discussed how to perform reproducible analysis in Rstudio with Rmarkdown using singularity containers.