Day 2 wrap up
In this session, we used a multi-sample gene count matrix generated by the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline to identify differentially expressed genes and functional enrichments. We worked in RStudio and performed exploratory data analysis, differential expression analysis, and functional enrichment analysis. In this lesson we will reflect on our results.
2.5.1 Exploratory analysis
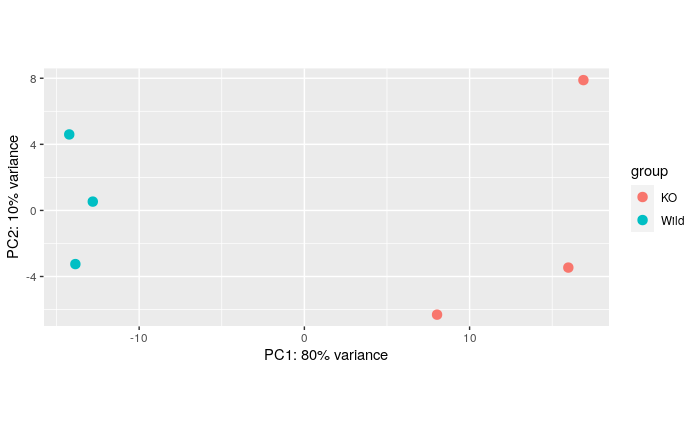
The principle component analysis shows a good separation of the sample across conditions on PC2 which accounts for the majority (80%) of variance. A clear separation of samples across conditions indicates differences in gene expression profiles between our samples are substantial and suggests the biological conditions we are comparing have a strong effect at the transcriptome level.
2.5.2 Differential expression analysis
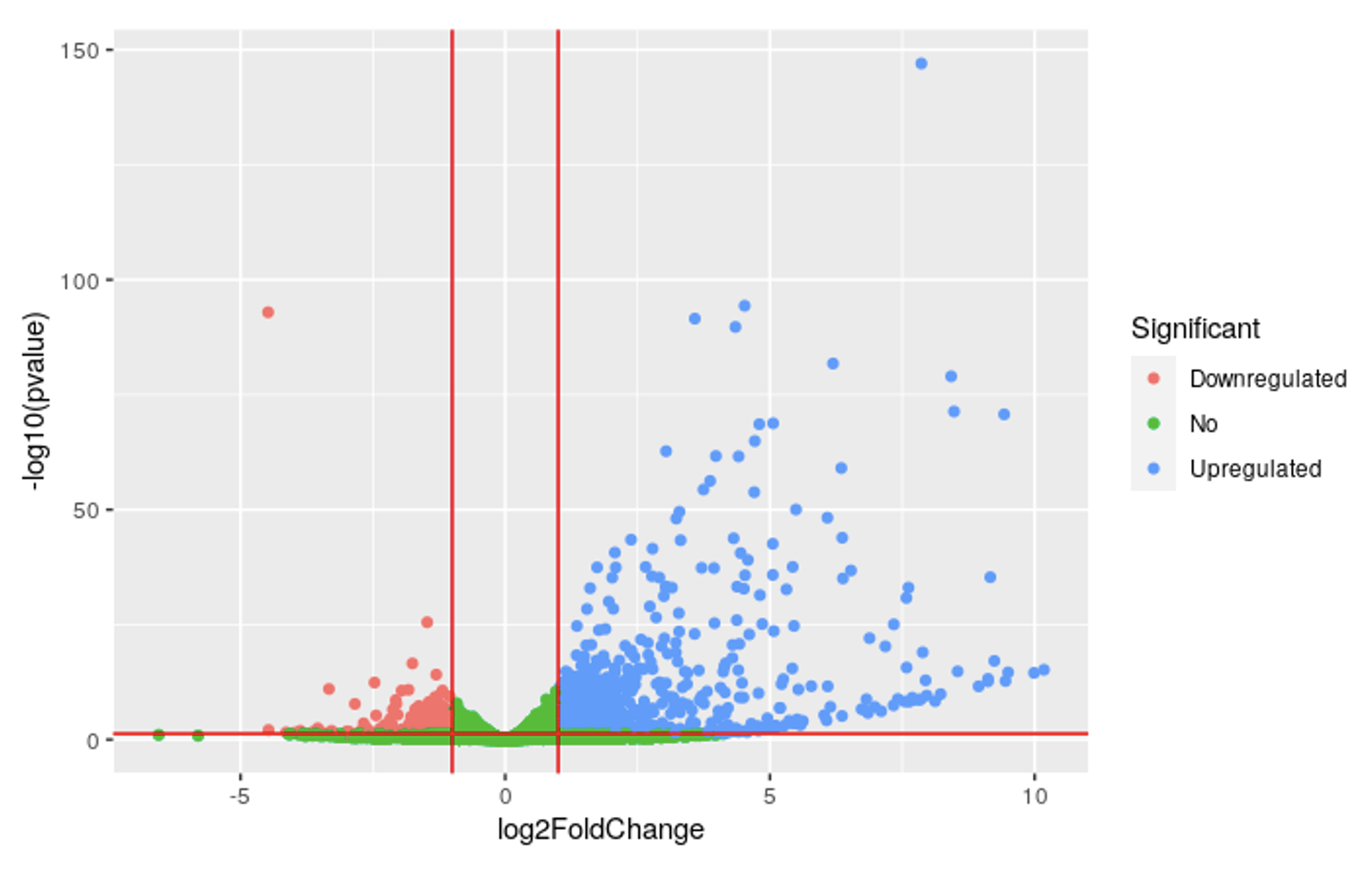
The Gtf2ird1 KO mice showed dysregulation of many genes. Out of the 19,859 genes in the mm10 mouse genome:
- 1,353 DE genes (6.8%) with a log-fold change (LFC) >0 were upregulated
- 984 DE genes (5%) with a LFC <0 were downregulated
This suggests that Gtf2ird1 plays a regulatory role on many genes in the mouse genome. The elevated number of upregulated genes may suggest that Gtf2ird1 function acts as a repressor for many genes or is involved in pathways that have a net repressive effect. These changes may result in observable phenotypic effects.
2.5.3 Functional enrichment analysis
Functional enrichment analysis revealed enrichment of multiple Gene Ontology (GO) categories:
- GO categories enriched in up-regulated genes: 823
- GO categories enriched in down-regulated genes: 255
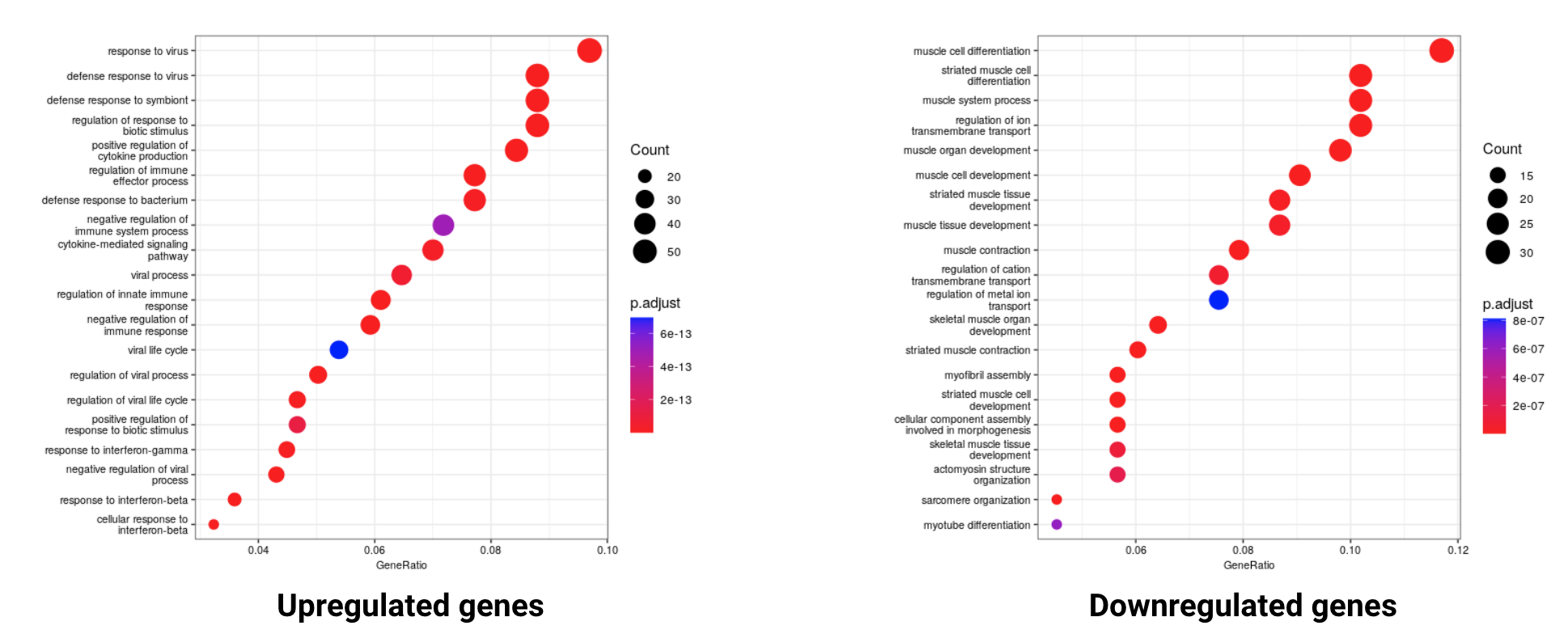
The most significantly enriched GO terms captured high-level biological functions that were not directly related to our phenotypes of interest. To make sense of these results, we need to examine the biological assumptions of our experiment. We identified a number of relevant GO terms relevant to this case study:
- Craniofacial development and distinctive facial features in WBS patients
- GO:0016055 Wnt signaling pathway (involved in cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion, differentiation of skin epithelial cells and the development of hair follicles).
- GO:0043588 skin development.
- GO:0008544 epidermis development.
- GO:0016055 Wnt signaling pathway (involved in cytoskeletal dynamics, cell adhesion, differentiation of skin epithelial cells and the development of hair follicles).
- Cardiovascular abnormalities in WBS patients
- GO:0014706 striated muscle tissue development.
- GO:0003012 muscle system process,
- GO:0055001 muscle cell development
- GO:0042692 muscle cell differentiation.
- GO:0045214 sarcomere organisation.
- GO:0014706 striated muscle tissue development.
2.5.4 Results from high-throughput experiments
We have the following two sets of results -
1. A list of differentially expressed (DE) genes.
2. A list of enriched functional categories (gene ontologies, pathways etc) which are derived from DE genes.
The results can be interpreted:
1. Based on prior expectations : You might expect to see a few genes changing as per your domain knowledge.
2. New discovery: Some results can be completely new and a result of changes related to cascading/compensating effects of the knockout, etc.
3. A combination of expectations plus discovery (1+2).
2.5.5 Experimental design limitations
In this experiment, we were unable to reliably comment on phenotypic changes relating to cognitive traits observed in patients with WBS. There were some other potentially limiting factors in our case study’s experimental design including:
- The choice of tissue: The lip epidermal tissue cannot reflect cognitive and neurological traits and is thus is a big limitation.
- The number of replicates: To improve statistical power and overcome any problems due to outliers, it is necessary to include more replicates per condition.