RNA-seq for differential expression workflow
Questions
- What are the different steps in a typical RNA-seq differential expression (DE) pipeline?
- What steps does the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline perform?
Now that we’ve learned about the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline, let’s think about where it sits within the broader experimental method. Remember we’re processing our RNA-seq reads so that we can identify differentially expressed genes and perform functional enrichment analysis.
The aim of our RNA-seq experiment is to determine which genes are differentially expressed between our two conditions of interest in our mice. We are then asking if the differences in expression between Gtf2ird1 knockout mice and normal (wildtype) mice can provide clues as to the underlying mechanisms involved in Williams-Beuren syndrome.
In order to identify differentially expressed genes between our groups of interest, we need to perform multiple steps that convert those raw sequence reads to analysis-ready data. We discussed the structure of this workflow and the various processes that are performed by nf-core/rnaseq pipeline earlier today.
Challenge
Here are all the steps that make up a typical differential expression workflow when we’re working with bulk RNA-seq data. Can you place the steps in the right order?
Hint: Start with the data given to you by a sequencing company and finish with the process you’d use to link expression differences with the phenotype of interest.
Solution
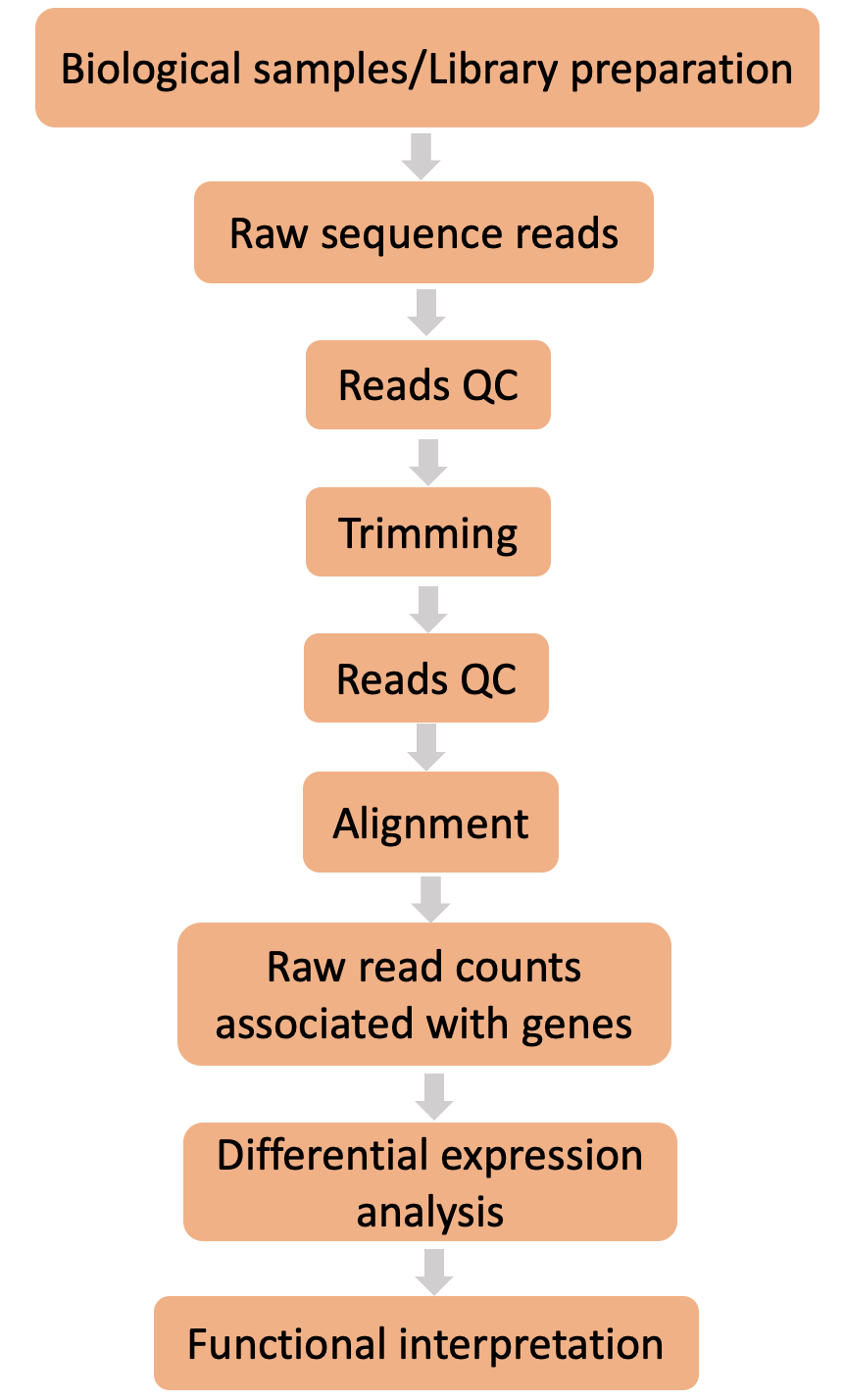
What steps does the nf-core/rnaseq pipeline perform?
The nf-core/rnaseq pipeline is designed to handle data processing steps that can easily be standardised and automated. It is used to process the raw sequence reads and generate read count data that we will be analysing tomorrow. These steps are often the most computationally challenging to perform.
Looking back up at the challenge exercise above can you recall some of the tools nf-core offers to perform the following steps?
- Raw reads quality control
- Read trimming
- Trimmed read quality control
- Read alignment
By now our nf-core/rnaseq command should have finished. Lets proceed to the next lesson, by clicking on What is nf-core/rnaseq doing? > nf-core/rnaseq results on the menu bar. Open your terminal window again to check the command has finished running.
Key points
- The main steps of a differential expression RNA-seq pipeline include quality control of raw data, alignment to a reference genome, measuring read counts associated with genes, differential gene expression analysis, and functional interpretation.
- The nf-core/rnaseq pipeline can be used to align raw sequence reads to a reference genome and generate read count data.
All materials copyright Sydney Informatics Hub, University of Sydney