Setup
1. Get a Google Account.
We will be utilising Google Colab, you will need a google account to use this service.
2. Get an Artemis Account
In the workshop you can make use of training account, but if you find yourself here in the future your unikey will require an Artemis account to complete the Artemis sections.
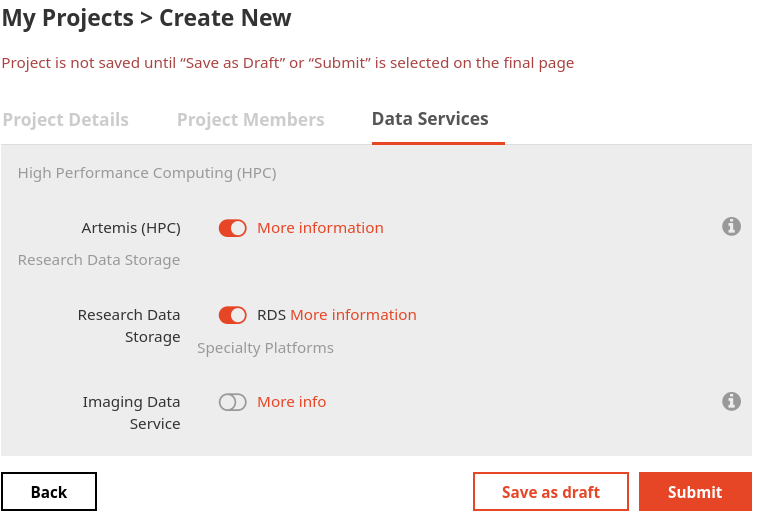
Artemis access is managed at a project level via dashr.sydney.edu.au. You can check current project access lists “Artemis (HPC)” under the “Research Services” section of your research data managment plan.

If your project does not have access either Edit an existing project or create a New Project and be sure to select Artemis (HPC) option in the “Data Services” tab.
Your Artemis account will be provisioned within a couple of days after it has been approved by your project’s Lead Chief Investigator.
Optional. Singularity Access on Artemis
If you require the Singularity versions of AlphaFold, please log a request to be given access to Singularity.
3. Get a shell terminal emulator
To connect to Artemis HPC, and follow this lesson, you will need a ‘terminal emulator’ program installed on your computer. Often just called a ‘terminal’, ‘shell terminal’, or ‘shell client’. Terminal emulators give you a window with a command line interface through which you can send commands to be executed by your computer.
A. Linux systems
If you use Linux, then chances are you already have a shell. Open your preferred terminal program and off you go! An X-Window server (X11) may also be useful if you want to be able to use GUIs.
Connection to Artemis can be made via ssh by issuing the following command on the shell:
ssh -X <unikey>@hpc.sydney.edu.auB. OSX (Mac computers and laptops)
Mac operating systems come with a terminal program, called Terminal. Just look for it in your Applications folder, or hit Command-Space and type ‘terminal’.
We also recommend installing XQuartz, which will replace OSX’s native X-Window server. XQuartz has some extra features that may offer better performance when using GUI programs. You’ll need to log out and back in again after installing XQuartz in order for it to activate.
Connection to Artemis can be made via ssh by issuing the following command in the terminal:
ssh -X <unikey>@hpc.sydney.edu.auC. Windows
Windows has a couple of terminal programs and shells buried in the Programs menu (cmd, powershell). However, those aren’t going to work for us, as you’ll need extra programs and utilities to connect to Artemis, such as an SSH implementation. To use Artemis on Windows, you have a couple of options:
Option i. PuTTY (Easy)
PuTTY, an SSH and telnet client, is a good simple option.
Head to the PuTTY Website and download PuTTY. You can install it to your computer, or just download the ‘binary’ and run it directly. Create a new session for use with Artemis as follows:
- Fill in the connection details:
- Host Name: hpc.sydney.edu.au
- Port: 22
- Connection type: SSH
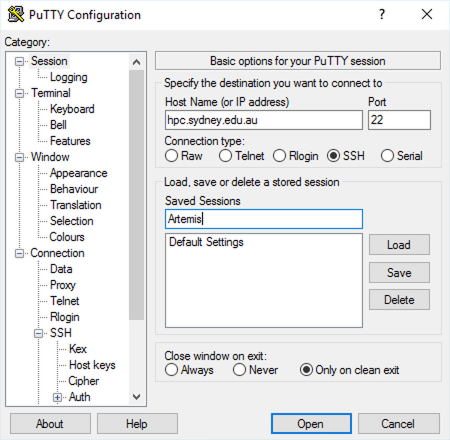
- Name this session “Artemis” and click ‘Save’
Note that PuTTY does not provide an X11 server natievly, so you won’t be able to use GUI programs on Artemis with just PuTTY. You can optionally install VcXsrv or similar to enable X-11 forwarding).
Option ii. WSL and Ubuntu (Advanced)
Install Ubuntu or some other Linux distro on the Windows Subsystem for Linux see here for details. This one will give you the full suite of Linux functions.
4. Off-campus access
If you’re attempting this training by yourself, or following on Zoom, off-campus then you’ll need to connect to the Sydney internet network before you can connect to Artemis.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a protocol that allows you to tap into a local private network remotely. Follow USyd Service Now instructions on the Cisco Any Connect VPN. Once you’ve connected to the VPN, the above connection methods will work, just as though you were on-campus.
5. Example scripts and data
Grab all the example scripts and data:
wget https://github.com/Sydney-Informatics-Hub/training.alphafold/raw/main/af_demo.zip
unzip af_demo.zip
cd af_demo